Eyes and The Parts of the Eye .....>
The Parts of the Eye
You can look at changed pieces of the eye by looking at your own eye in the mirror or by looking at (yet not contacting) a companion's eye. A portion of the eye's parts are anything but difficult to see, so most companions will say OK. Most companions won't state OK on the off chance that you request to see their liver!
Large as a Ping Pong Ball
The eye is about as large as a ping-pong ball and sits in a little empty region (the eye attachment) in the skull. The eyelid secures the front piece of the eye. The top helps keep the eye perfect and wet by opening and closing a few times each moment. This is called squinting, and it's both a willful and automatic activity, which means you can flicker at whatever point you need to, yet it likewise occurs without you in any event, pondering it.The eyelid additionally has extraordinary reflexes, which are programmed body reactions, that secure the eye. At the point when you step into splendid light, for instance, the eyelids press together firmly to ensure your eyes until they can change in accordance with the light. Also, on the off chance that you ripple your fingers close (however not very close!) to your companion's eyes, you'll make certain to see your companion's eyes flicker. Your companion's eyelids shut consequently to shield the eye from conceivable threat. Furthermore, talking about shuddering, remember eyelashes. They work with the eyelids to keep soil and other undesirable stuff out of your eyes.
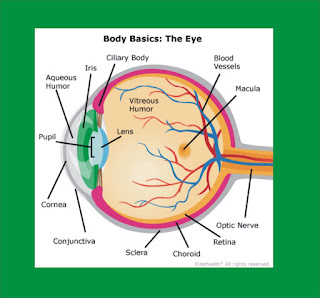
The white piece of the eyeball is known as the sclera (state: SKLAIR-uh). The sclera is made of an extreme material and has the significant activity of covering the vast majority of the eyeball. Think about the sclera as your eyeball's external coat. Look carefully at the white of the eye, and you'll see lines that resemble minor pink strings. These are veins, the minor cylinders that convey blood, to the sclera.
The cornea (state: KOR-nee-uh), a straightforward vault, sits before the shaded piece of the eye. The cornea enables the eye to center as light clears its path through. It is a significant piece of the eye, however you can barely observe it since it's made of clear tissue. Like clear glass, the cornea gives your eye an unmistakable window to see the world through.
Iris Is The Colorful Part
Behind the cornea are the iris, the understudy, and the foremost chamber. The iris (state: EYE-riss) is the bright piece of the eye. At the point when we state an individual has blue eyes, we truly mean the individual has blue irises! The iris has muscles joined to it that change its shape. This enables the iris to control how a lot of light experiences the student (state: PYOO-pul).The understudy is the dark hover in the focal point of the iris, which is extremely an opening in the iris, and it gives light a chance to enter the eye. To perceive how this functions, utilize a little electric lamp to perceive how your eyes or a companion's eyes react to changes in splendor. The understudies will get littler when the light sparkles close to them and they'll open more extensive when the light is no more.
The foremost (state: A teer-ee-ur) chamber is the space between the cornea and the iris. This space is loaded up with an extraordinary straightforward liquid that feeds the eye and keeps it solid.
Light, Lens, Action
These next parts are truly cool, however you can't see them with simply your own eyes! Specialists utilize extraordinary magnifying instruments to take a gander at these inward pieces of the eye, for example, the focal point. After light enters the student, it hits the focal point. The focal point sits behind the iris and is clear and dreary. The focal point's main responsibility is to concentrate light beams on the back of the eyeball — a section called the retina (state: RET-I-nuh).The focal point works a lot of like the focal point of a motion picture projector at the motion pictures. Next time you sit in obscurity theater, look behind you at the flood of light originating from the projection stall. This light experiences a ground-breaking focal point, which is centering the pictures onto the screen, so you can see the film unmistakably. In the eye's case, nonetheless, the film screen is your retina.
Your retina is in the exceptionally back of the eye. It holds a great many cells that are delicate to light. The retina takes the light the eye gets and transforms it into nerve flag so the mind can comprehend what the eye is seeing.


Comments
Post a Comment